(Authored by:-Ar. Bhupendra Kumar, Founder Aeiforia)
Ancient India was a vast and diverse region, stretching from the Himalayan mountains in the north to the Deccan Plateau in the south. It was divided into numerous kingdoms and empires, each with their own territories, languages, and cultural practices. During this period, the Indian subcontinent witnessed significant cultural, religious, and political developments, leaving behind a rich legacy of art, architecture, literature, and philosophy.
Ancient Indian architecture is renowned for its grandeur and opulence. It is diverse and encompasses a wide range of styles, each showcasing a unique architectural marvel. From the majestic temples of south India to the intricate palaces of north India, ancient Indian architecture is a testament to the brilliance and creativity of our ancestors.
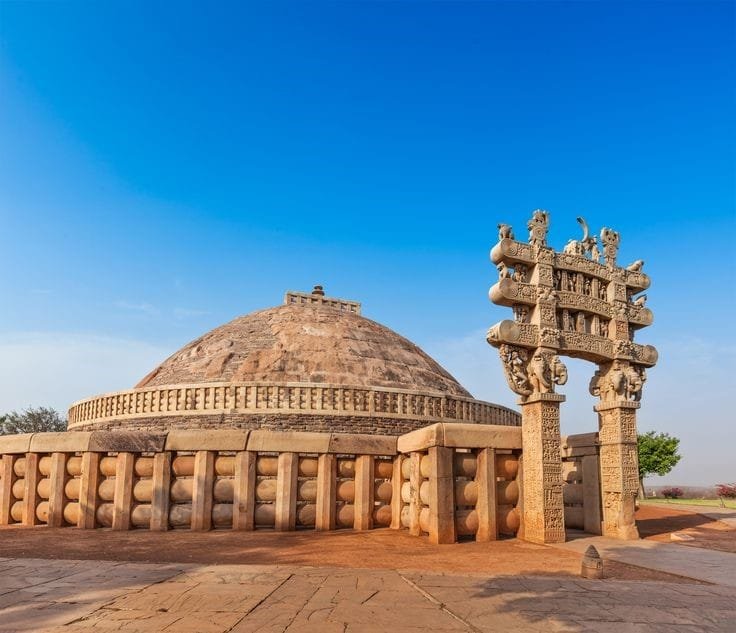
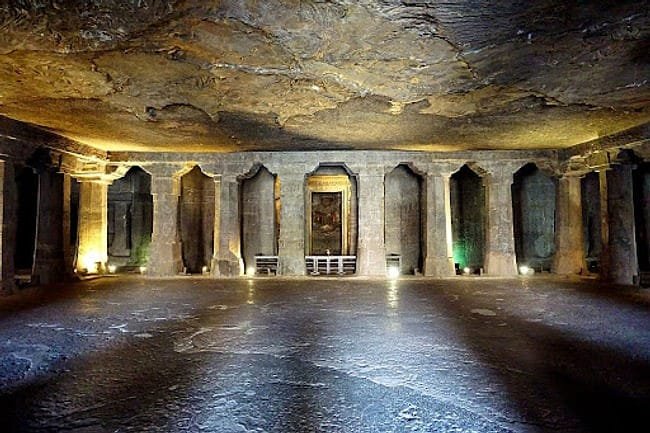
As for temples, they always make a statement about devotion and architectural skills of the artisans. Their intricate carvings, sculptures, and designs are simply breathtaking. Stupas and viharas are another important form of architecture in ancient India. Stupas are commemorative structures built to honor the dead and contain relics of the Buddha and other revered figures. They typically consist of a dome-shaped structure, often surrounded by geometric patterns and built at a high point, symbolising the achievement of enlightenment. Viharas, on the other hand, are monasteries where Buddhist monks lived and studied having a complex layout, including accommodation for the monks, shrines, and meditation halls.
Furthermore, a unique way of incorporating light into buildings was prevalent at that time. People used to utilise skylights and domed structures to channel light evenly throughout the buildings. Skylights, which were strategically placed on the roofs, allowed sunlight to filter through, illuminating the interiors. Domes, with their curved surfaces, captured and reflected light, creating a mesmerising effect. These architectural elements not only enhanced the beauty of the structures but also provided natural light without the need for artificial lighting.
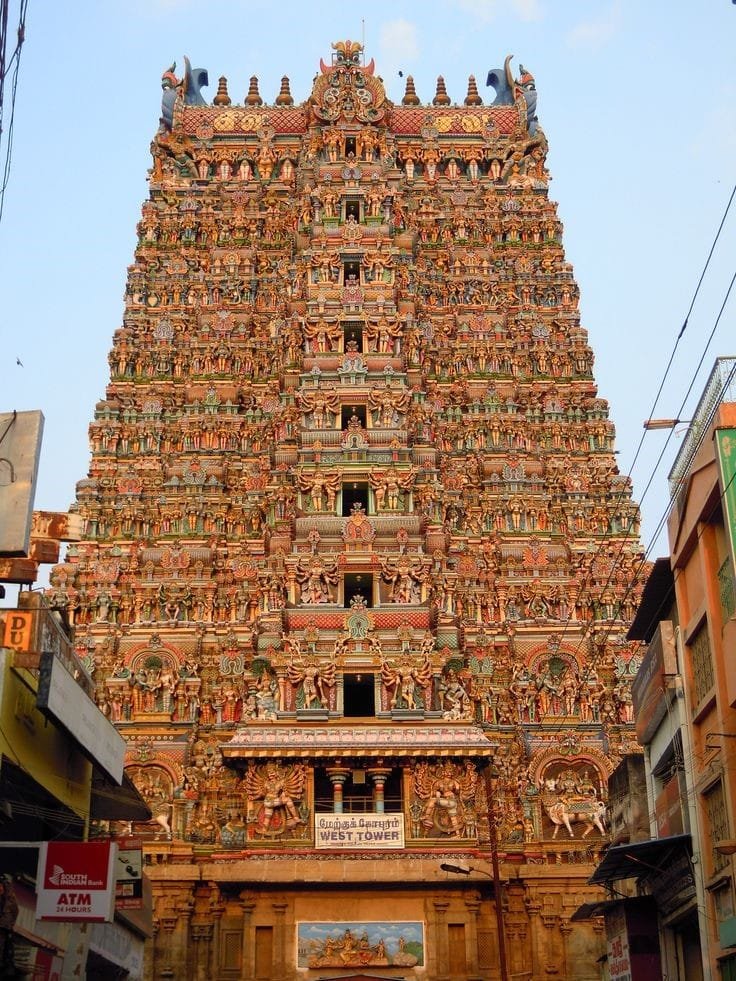
Let’s discuss about Meenakshi Temple, located in Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India, and considered one of the most significant temples of India. It was built over a period of 21 years, starting in 1569 CE, by King Thirumalai Nayak in the 16th century. The temple complex covers an area of about 14 hectares consisting of various shrines, halls, and courtyards. A blend of traditional Dravidian style with the elements of Hindu and Islamic styles, the temple is constructed with towering gopurams, intricate carvings and rich history attracting millions of visitors each year.
The ancient civilization was also known for its advanced urban planning and infrastructure. Skilled architects designed cities with efficient layouts, including wide streets, well-planned residential areas, and public amenities such as markets, gardens, and places of worship.
Moving ahead, fort architecture in India was crucial in protecting the boundaries of kingdoms and cities. These structures were not only military fortifications but also centres of administration, trade, and cultural exchange, indeed a symbol of power and grandeur.
Thus, ancient Indian architecture is a testament to the rich cultural and architectural heritage of the country. Its diverse styles, intricate designs, and grand structures have left an indelible mark on the world. From the majestic temples to the bustling cities, ancient Indian architecture is a testament to the craftsmanship and creativity of its builders.
Meenakshi Temple

Source- https://www.flickr.com/photos/zoearnold12/7187825077/in/photostream/
Sanchi Stupa

Source – https://in.pinterest.com/pin/762234305701854326/
Viharas

Source- https://prepp.in/news/e-492-viharas-art-and-culture-notes
Showcase the advanced engineering and artistic skills of ancient India.
Ajanta Caves